MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
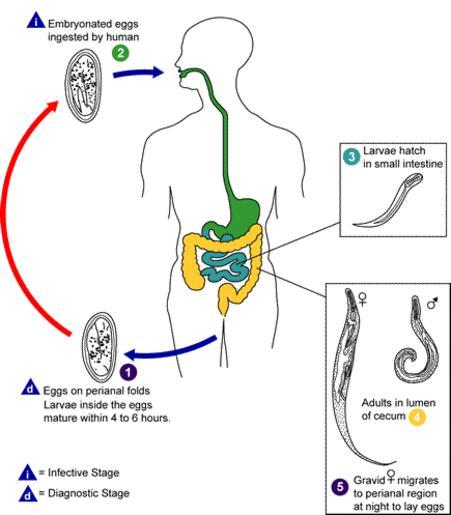
| View Original: | Enterobius_vermicularis_LifeCycle.gif (435x497) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
| Keywords: Enterobius vermicularis LifeCycle.gif Enterobiasis Enterobius vermicularis Life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis 1 Eggs are deposited on perianal folds <br /> 2 Self-infection occurs by transferring infective eggs to the mouth with hands that have scratched the perianal area <br /> 3 Person-to-person transmission can also occur through handling of contaminated clothes or bed linens Enterobiasis may also be acquired through surfaces in the environment that are contaminated with pinworm eggs e g curtains carpeting Some small number of eggs may become airborne and inhaled These would be swallowed and follow the same development as ingested eggs Following ingestion of infective eggs the larvae hatch in the small intestine <br /> 4 and the adults establish themselves in the colon <br /> 5 The time interval from ingestion of infective eggs to oviposition by the adult females is about one month The life span of the adults is about two months Gravid females migrate nocturnally outside the anus and oviposit while crawling on the skin of the perianal area The larvae contained inside the eggs develop the eggs become infective in 4 to 6 hours under optimal conditions <br /> 1 Retroinfection or the migration of newly hatched larvae from the anal skin back into the rectum may occur but the frequency with which this happens is unknown http //www dpd cdc gov/dpdx/images/ParasiteImages/A-F/Enterobiasis/Enterobius_LifeCycle gif Centers for Disease Control Prevention CDC http //www dpd cdc gov/dpdx PD-USGov Enterobius vermicularis LifeCycle-gl gif Image Enterobius vermicularis LifeCycle B svg only legends ; Image Enterobius vermicularis LifeCycle pt-version svg portuguese version Enterobius v life cycle CDC lifecycles | ||||