MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
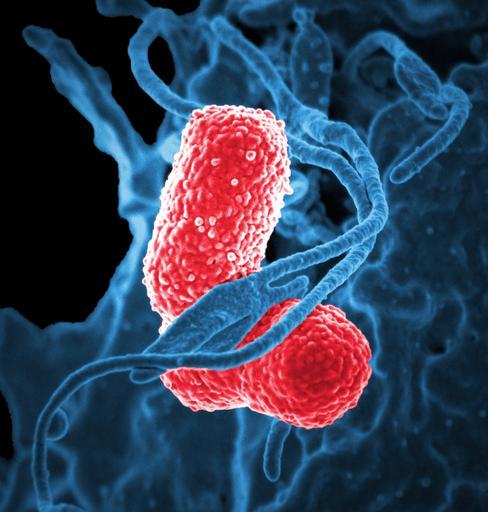
| View Original: | Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniaeand neutrophil.bmp.jpg (732x768) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
| Keywords: Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniaeand neutrophil.bmp.jpg en Produced by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases NIAID this digitally-colorized scanning electron micrograph SEM depicts a blue-colored human white blood cell WBC known specifically as a neutrophil interacting with two pink-colored rod-shaped multidrug-resistant MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria which are known to cause severe hospital-acquired nosocomial infections Please see the Flickr link below for additional NIAID photomicrographs of various bacteria Klebsiella is a type of Gram-negative bacteria that can cause different types of healthcare-associated infections including pneumonia bloodstream infections wound or surgical site infections and meningitis Increasingly Klebsiella bacteria have developed antimicrobial resistance most recently to the class of antibiotics known as carbapenems Klebsiella bacteria are normally found in the human intestines where they do not cause disease They are also found in human stool feces In healthcare settings Klebsiella infections commonly occur among sick patients who are receiving treatment for other conditions Patients whose care requires devices like ventilators breathing machines or intravenous vein catheters and patients who are taking long courses of certain antibiotics are most at risk for Klebsiella infections Healthy people usually do not get Klebsiella infections 2014 http //phil cdc gov/phil/details asp David Dorward; Ph D ; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases other versions Custom license marker 2015 05 13 http //phil cdc gov/phil/details asp David Dorward; Ph D ; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Uploaded with UploadWizard Scanning electron microscopic images | ||||