MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
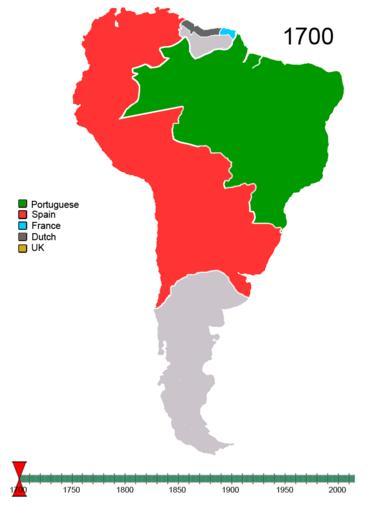
| View Original: | Non-Native American Nations Control over South America 1700 and on.gif (800x1100) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
| Keywords: Non-Native American Nations Control over South America 1700 and on.gif right border 0 style border 1px solid 000000; +Nations and flags in South America - colspan 4 Former nations of South America - ffff00 width 30 10 Entre RĂos 25px - ffff00 width 30 10 Juliana Republic 25px - ffff00 width 30 10 Gran Colombia 25px - ff00ff width 30 10 Liga Federal 25px - ff6666 width 30 10 Riograndense Republic 25px - 009900 width 30 10 Colonial Brazil; United Kingdom of Portugal Brazil and the Algarves 25px - ff3333 width 30 10 Viceroyalty of Peru Viceroyalty of New Granada 25px - colspan 4 Present day nations of South America - 0000cc width 30 10 Argentina Argentina -LOCOMBIA 333333 width 30 10 Bolivia Bolivia - 33cc33 width 30 10 Brazil Brazil - 00ff00 width 30 10 Chile Chile - ffff00 width 30 10 Colombia Colombia - cc0000 width 30 10 Ecuador Ecuador - 00ccff width 30 10 French Guiana France France - ff3300 width 30 10 Netherlands the Netherlands - 663333 width 30 10 Guyana Guyana - 006666 width 30 10 Paraguay Paraguay - 993333 width 30 10 Peru Peru - 000000 width 30 10 Suriname Suriname - cc9933 width 30 10 Britain 25px - 990000 width 30 10 Uruguay Uruguay - 333399 width 30 10 Venezuela Venezuela - colspan 4 Flags used are flags of present day countries <br>or the last flag used by a now-defunct nation Notes islands close to South America aren't included as this is a map about continental South America Not all borders are to scale with some being changed to be easier to see When a political change is too small to notice a small note is added to help point to the change When referring to countries the most common or modern name is used ”i e England instead of the United Kingdom After the 1940s Ecuadorian-Peruvian war a new border was demarcated between Ecuador and Peru However between 1943 and 1946 the United States Air Force performed several aerial reconnaissance missions over the Cordillera del CĂłndor region losing 2 aircraft and 14 men in accidents to help in the demarcation efforts They found that the Cenepa river was much longer than previously thought and that it runs between the Zamora and the Santiago This finding conflicted with article VIII point B-1 of the Rio Protocol which laid out delineation of the border for that area as follows From the Quebrada de San Francisco the watershed between the Zamora and Santiago Rivers to the confluence of the Santiago River with the Yaupi; article VIII point B-1 of the Rio Protocol The difficulty was that there is not one watershed between the Zamora and the Santiago but two as interpreted by Ecuador This resulted in Ecuadorian president Galo Plaza halting demarcation in 1949 About 78 kilometers of border were left unmarked These 78 km are still in dispute but are too small to be shown on the map Portuguese During the first two centuries of the colonial period attracted by the vast natural resources and untapped land other European powers tried to establish colonies in several parts of Brazilian territory in defiance of the papal bull and the Treaty of Tordesillas which had divided the New World into two parts between Portugal and Spain Colonial Brazil was Portuguese French colonists tried to settle in present-day Rio de Janeiro from 1555 to 1567 the so-called France Antarctique episode and in present-day SĂŁo LuĂs from 1612 to 1614 the so called France Équinoxiale After several years of open warfare the Dutch formally withdrew in 1661 Little French and Dutch cultural and ethnic influences remained of these failed attempts thumb Spanish The New Kingdom of Granada Spanish Nuevo Reino de Granada was the name given to a group of 16th century Spanish colonial provinces in northern South America corresponding mainly to modern Colombia It became part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717 Viceroyalty of Peru ruled the Southern part of the Spanish Empire Dutch At the Treaty of Breda in 1667 the Dutch decided to keep the nascent plantation colony of Suriname conquered from the British while leaving the small trading post of New Amsterdam in North America now New York City in the hands of the British Guyana Lord Willoughby famous in the early history of Barbados also turned his attention to Guiana and founded a settlement in Suriname in 1651 This was captured by the Dutch in 1667 and though later recaptured by the British it was ceded to the Dutch at the Peace of Breda 1667 French Francais In 1667 the British took French Guiana Following the Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667 the area was given back to the France folk The Dutch briefly occupied it for a period in 1676 though they occupied Cayenne from 1664 “76 Mapuche The Mapuche successfully resisted many attempts by the Inca Empire to subjugate them despite their lack of state organisation They fought against the Sapa Inca Tupac Yupanqui and his army The result of the bloody three day confrontation known as the Battle of the Maule was that the Inca conquest of the territories of Chile ended at the Maule river Here they were forced to establish a fortified border They fought against the Spaniards for over 300 years Initial conquests of land by Spain in the late 16th century were repelled by the Mapuche so effectively that there were areas to which Europeans did not return until late in the 19th century One of the main geographical boundaries was the BĂo-BĂo River which the Mapuche used as a natural barrier to Spanish and Chilean incursion The 300 years were not uniformly a period of hostility but often allowed substantial trade and interchange between Mapuche and Spaniards or Chileans Nevertheless the long Mapuche resistance has become primarily known as the War of Arauco and is immortalized in Alonso de Ercilla's epic poem La Araucana 1750 The King of Spain was the nominal ruler of the Misiones Orientales and in the Treaty of Madrid 1750 he gave the eastern part of the Jesuit Reductions to Portugal The seven Jesuit missions here were to be dismantled and relocated on the Spanish western side of the Uruguay River The Guarani people living here refused which led to the Guarani War won by the Portuguese and Spanish people 1777 Misiones Orientales returned to Spain in 1777 in the First Treaty of San Ildefonso 1796 Britain took Guyana from the Dutch in 1796 1801 Misiones Orientales ceded to Portugal in the Treaty of Badajoz 1801 1802 Dutch retake Guyana in 1802 1803 Guyana is retaken by the British 1809 In 1809 an Anglo-Portuguese naval squadron took French Guiana ousting governor Victor Hugues and gave it to the Portuguese in en Brazil However with the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1814 the region was handed back to the French though a Portuguese presence remained until 1817 1810 thumb en Liga Federal Liga de los Pueblos Libres marked in RED in 1815 the United Provinces of the RĂo de la Plata in BLUE United Provinces of South America Spanish Provincias Unidas de Sud AmĂ©rica was the union founded in 1810 as a result of the independence of the southernmost part of South America from Spain It would later become known as Argentina 1811 Against the background of rebellions in many parts of the former Viceroyalty of the RĂo de la Plata Portugal annexed the province of Rio Grande do Sul and the Misiones Orientales now part of Rio Grande do Sul 1811 Paraguay declares independence 1814 However with the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1814 French Guiana was handed back to the French though a Portuguese presence remained until 1817 1815 The Liga Federal or Liga de los Pueblos Libres was created in 1815 by the provinces of CĂłrdoba Corrientes Republic of Entre RĂos Misiones Santa Fe and the Provincia Oriental what would become later Uruguay it was led by JosĂ© Gervasio Artigas in opposition to the unitarists and dissolved in 1820 <GALLERY> Image Liga de los Pueblos Libres - en - League of the Free Peoples png </GALLERY> 1818 Intermittent warfare against Spain and Chile continued until 1817 when an army led by Bernardo O'Higgins Chile's most renowned patriot and JosĂ© de San MartĂn hero of the Argentine War of Independence crossed the Andes into Chile and defeated the royalists On February 12 1818 Chile was proclaimed an independent republic under O'Higgins' leadership The political revolt brought little social change however and 19th century Chilean society preserved the essence of the stratified colonial social structure which was greatly influenced by family politics and the Roman Catholic Church A strong presidency eventually emerged but wealthy landowners remained extremely powerful 1819 SimĂłn BolĂvar the Liberator of Spanish South America and other revolutionaries in the First Venezuelan Republic occasionally used the term Colombia as a reference to all of Spanish America until the proclamation of a republic under that name in 1819 at the Congress of Angostura 1820 The Republic of Entre RĂos was a short-lived republic in South America in the early nineteenth century Comprising approximately 83 000 km² 32 000 square miles of what are today the Argentinian provinces of Entre RĂos and Corrientes the country was founded in 1820 by the caudillo General Francisco RamĂrez who styled himself jefe supremo and lasted only one year The United Provinces of the RĂo de la Plata officially incorporate the Falkland Islands into their territory where name an administrative government for the islands The colonel David Jewett is replaced by Guillermo Mason 1821 In 1821 after the defeat of Artigas and his Liga Federal nation in Battle of TacuarembĂł and with the support of the local aristocratic families the Provincia Oriental modern day Uruguay was annexed by Portugal under the name of ProvĂncia Cisplatina giving the country a strategic position over the RĂo de la Plata and control over the United Provinces' main port San MartĂn who had displaced the royalists of Chile after the magnificent battle of the Andes and who had disembarked in Paracas in 1819 proclaimed the independence of Peru in Lima on July 28 1821 with the words From this moment on Peru is free and independent by the general will of the people and the justice of its cause that God defends Long live the homeland Long live freedom Long live our independence 1822 On October 9 1820 Guayaquil became the first city in Ecuador to gain its independence from Spain It was not until May 24 1822 that the rest of Ecuador gained its independence after Field Marshal Antonio JosĂ© de Sucre defeated the Spaniard Royalist forces at the Batalla del Pichincha Battle of Pichincha near Quito Following the battle Ecuador joined SimĂłn BolĂvar's Republic of Gran Colombia Brazil achieved its independence from Portugal on September 7 1822 On October 12 1822 Dom Pedro became the first Emperor of Brazil being crowned on December 1 1822 Portugal would recognize Brazil as an independent country in 1825 1825 SimĂłn BolĂvar who had liberated Audiencia de Charcas and destroyed the last remnants of the Spanish army did not approve of an union with Peru and urged the creation of a separate and independent state Thus the new Republic of Bolivia named in his honor was born with BolĂvar as its first president From 1825 to 1828 Banda oriental was part of the Provincias Unidas del RĂo de la Plata 1828 The Argentina-Brazil War War saw that neither side gained the upper hand and in 1828 the Treaty of Montevideo fostered by the United Kingdom gave birth to Uruguay as an independent state The nation's first constitution was adopted on July 18 1830 1829 The Buenos Aires government creates the Falkland Islands Political and Military Command extending the licenses of the settlers 1830 The federation finally dissolved during the rest of 1830 and was formally abolished in 1831 as Venezuela Ecuador and New Granada came to exist as independent states 1833 As part of the Conquest of the Desert in 1833 coordinated offensives by Juan Manuel de Rosas in Buenos Aires Province and other military leaders in the Cuyo region attempted to exterminate resistant tribes but only Rosas had any success The United Kingdom takes control over the Falkland Islands 1836 Marshal AndrĂ©s de Santa Cruz promoted an ambitious project to reunite these two territories on the basis of a confederacy The Peru-Bolivian Confederation was a plan that attempted to reunite the Alto PerĂş Upper Peru now Bolivia and Bajo Peru Lower Peru now simply Peru into a single political and economic entity Peru-Bolivian Confederation This integration was based not only on historical cultural and ethnic reasons but also on sound economic motives The union was trying to restore the ancient commercial routes and promote a policy of open markets In Peru he began by having an assembly proclaim on March 17 1836 the Republic of South Peru followed on August 11 1836 by a similar proclamation of the Republic of North Peru In each case he became the new state's supreme protector see protector title for similar titles a president with full powers The Riograndense Republic often called Piratini Republic Portuguese RepĂşblica Rio-Grandense or RepĂşblica do Piratini was a separatist state that existed between September 11 1836 and March 1 1845 where nowadays is the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil It voted itself a Constitution in 1843 Independence was proclaimed by en AntĂ´nio de Souza Netto who assigned en Bento Gonçalves da Silva as its first president during the rebellion which became the en War of Tatters It was led mostly by foreigners who had fought in the Argentina-Brazil War generals who decreed that no compromise could be reached between the Brazilian Empire and Republican forces 1839 The Peru-Bolivian Confederation was a loose union between the states of Peru by this time divided into a Republic of North Peru and a Republic of South Peru which included the capital Tacna and Bolivia The Confederation fell apart after being defeated by a combined Chilean and Peruvian Force in what it is now known as the War of the Confederation The Juliana Republic was declared in the Brazilian province of Santa Catarina on July 24 1839 and which lasted up to November 15 1839 It was an extension of the War of Tatters in the neighbouring province of Rio Grande do Sul where the Riograndense Republic had been declared 1840 thumb A map of the British colony Guyana was published in 1840 Venezuela protested claiming the entire area west of the Essequibo River 1845 The Riograndense Republic had five capitals during its nearly nine years of existence the cities of Piratini for which it is often called Piratini Republic Alegrete Caçapava do Sul official capitals BagĂ© for only two weeks and SĂŁo Borja The war between the GaĂşchos and the Brazilian Empire was ended by the Ponche Verde Treaty 1843 On the year 1843 the Chilean government sent an expedition with the appointed task of establishing a permanent settlement Punta Arenas on the shores of the Strait of Magellan 1860 While visiting the region in 1860 Orelie-Antoine came to sympathise with the Mapuche cause and a group of loncos Mapuche tribal leaders in turn elected him to the position of King ”possibly in the belief that their cause might be better served with a European acting on their behalf Orelie-Antoine then set about establishing a government for his nation Kingdom of Araucania and Patagonia created a blue white and green flag and had coins minted for the nation under the name of Nouvelle France 1862 In 1860 Chilean president JosĂ© JoaquĂn PĂ©rez Mascayano decided to incorporate the AraucanĂa With the proclamation of Kingdom of Araucania and Patagonia by a French lawyer Orelie-Antoine it became a priority and a pretext to incorporate the AraucanĂa even though the Kingdom never in fact became a serious threat to the Chilean or Argentine state Gen Saavedra advanced in relatively short time to the Malleco River and there founded the city of Angol together with the forts of MulchĂ©n and Lebu in the year 1862 1866 National borders between Bolivia and Chile had not been clearly agreed until 1866; the two countries had negotiated a treaty that established the 24th parallel as their boundary and entitled Bolivia and Chile to share in tax revenue on mineral exports out of the territory between the 23rd and 25th parallels 1867 Bolivia is forced to sign an unfavorable treaty with Brazil ceding 300 000 square kilometers 115 830 square miles that had provided easy access to the Amazon and Plate river systems 1870 thumb The War of the Triple Alliance also known as the Paraguayan War and the Great War by the Paraguayans was fought from 1864 to 1870 and caused more deaths than any other South American war It was fought between Paraguay and the allied countries of Argentina Brazil and Uruguay In total Argentina and Brazil annexed about 140 000 km² 55 000 square miles of Paraguayan territory Argentina took much of the Misiones region and part of the Chaco between the Bermejo and Pilcomayo rivers an area which today constitutes the province of Formosa; Brazil enlarged its Mato Grosso province by claiming territories that had been disputed with Paraguay before the war Both demanded a large indemnity which was never paid and occupied Paraguay until 1876 Meanwhile the Colorados had gained political control of Uruguay which they retained until 1958 1874 A second treaty in 1874 superseded this entitling Bolivia to collect full tax revenue between the 23rd and 24th parallels but fixed tax rates on Chilean companies for 25 years Bolivia subsequently became dissatisfied at the arrangement as Chilean interests backed by British capital quickly expanded and controlled the mining industry and feared Chilean encroachment on its coastal region 1881 200px thumb left As the Andes are split by fjords and channels the southernmost parts of the Chile-Argentina border are mostly defined by parallels and meridians Victory was however a mixed blessing During the war Chile waived most of its claim over Patagonia in 1881 to ensure Argentina's neutrality In order to avoid fighting Argentina as well Chilean President AnĂbal Pinto authorized his envoy Diego Barros Arana to hand over as much territory as was needed to avoid Argentina siding with Bolivia and Peru Barros succeeded in his mission Argentina received the Atlantic coast and Chile the Pacific coast However border disputes continued as Patagonia was still an unexplored area The definition of the border used in 1881 established the highest mountains that divides the drainage basins to the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic as border This concept was easy to apply in northern regions but in Patagonia drainage basins crossed the Andes; this led to dispute what over the highest peaks would the frontier or the drainage basins In 1902 war was again avoided when British King Edward VII agreed to mediate between the two nations He established the current border in the Patagonia region in part by dividing many disputed lakes into two equal parts most of these lakes still have one name on each side of the frontier 1883 <GALLERY> Image War of the Pacific LOC map png Image Guerra-del-pacifico-01-a svg Image Change of Chile frontier border in the Occupation of the AraucanĂa - 1870 jpg </GALLERY> Peru was defeated by Chile in the 1879 “1883 War of the Pacific losing the provinces of Arica and Tarapacá in the treaties of AncĂłn and Lima At the same time Chile finishes the Occupation of Araucania 1884 Roca followed Nicolás Avellaneda as president of Argentina He thought it was imperative to conquer the territory south of the Negro River as soon as possible and ordered the 1881 campaign under the control of colonel Conrado Villegas Within a year Villegas conquered the NeuquĂ©n Province he reached the Limay River The campaign continued to push the aboriginal resistance further south to fight the last battle on October 18 1884 The last rebel group of over 3 000 members under the command of caciques Inacayal and Foyel surrendered two months later in present Chubut Province 1895 With a victorious Chilean army returning from the War of the Pacific the government of Domingo Santa MarĂa launched into a final campaign to incorporate the heartland of the Mapuches into Chile The colonel Gregorio Urrutia was chosen for this task The old Spanish town of Villarrica was founded anew and the forts of Carahue Lautaro Pillánlelbu Temuco Nueva Imperial and PucĂłn established The tribes living close to these forts lost their territory and about ten-thousand Mapuche Indians were killed in skirmishes with the Chilean army Many of the survivors escaped to the mountains wherein they joined with the Pehuenches and the other tribes which were in flight from the Argentine territory to the east Some indigenous remnants were placed into reductions and their land given to both Chilean and other settlers of foreign nationality Some historians consider the occupation of the Araucania to be the end of a 300-years long War of Arauco 1899 An international tribunal arbitrate the boundary in 1897 For two years the tribunal consisting of two Britons two Americans and a Russian studied the case Their three-to-two decision handed down in 1899 awarded 94 percent of the disputed territory to Guyana 1902 In 1902 war was again avoided between Chile and Argentina when British King Edward VII agreed to mediate between the two nations He established the current border in the Patagonia region in part by dividing many disputed lakes into two equal parts most of these lakes still have one name on each side of the frontier 1903 Bolivia also lost the state of Acre known for its production of rubber when Brazil persuaded the state of Acre to secede from Bolivia in 1903 see the Treaty of PetrĂłpolis 1922 Another dispute was created after the signing of the Treaty of SalomĂłn-Lozano in March 1922 which favoured Colombia at the expense of both Peru and Ecuador The border dispute with Colombia involved territory in the rubber-tapping region between the RĂo Caquetá and the northern watershed of the RĂo Napo It established the Putumayo River as the boundary between Colombia and Peru Although it was unpopular in Peru President Augusto B Leguia accepted it under considerable pressure from the United States 1929 The disputed area between Chile and Peru is finally decided giving half to Peru and half to Chile 1935 thumb By the time a ceasefire was negotiated on June 10 1935 Paraguay controlled most of the region This was recognized in a 1938 truce signed in Argentina by which Paraguay was awarded three-quarters of the Chaco Boreal Bolivia did get a small strip of land that bordered the Paraguay River's Puerto Busch Some years later it was found that there were no oil resources in the Chaco proper 1936 Ulloa-Viteri Accord This agreement established a status quo border line based on the effective possession of territory that Peru and Ecuador had in the Amazon region at the time This border was very similar to that established by the Rio de Janeiro Protocol 5 years later To Ecuador the status quo line simply demonstrated how much territory Peru had taken from Ecuador in the preceding century Ecuador never considered this agreement a final treaty of borders and continued its fight which were based on Gual-Larrea and Pedemonte-Mosquera 1942 During the course of the war between Ecuador and Peru Peru gained control over all the disputed territory and occupied the Ecuadorean province of El Oro north of what is now Tumbes and some parts of the province of Loja 65 percent of the former country demanding that the Ecuadorean government give up its territorial claims The Peruvian Navy blocked the port of Guayaquil cutting supplies to the Ecuadorean troops After a few weeks of war and under pressure by the U S and several Latin American nations all fighting came to a stop Ecuador and Peru came to an accord formalized in the Rio Protocol signed on January 29 1942 in favor of hemispheric unity against the Axis Powers in World War II As a result of its victory Peru was awarded the disputed territory 1966 Guyana achieved independence on May 26 1966 and became the Co-operative Republic of Guyana on February 23 1970 - the anniversary of the Cuffy slave rebellion - with a new constitution 1975 In 1973 the local government led by the NPK a largely Creole meaning ethnically African or mixed African-European party started negotiations with the Dutch government leading towards full independence of Suriname which was granted on 25 November 1975 See Also Hispanic American wars of independence <GALLERY> File Non-Native American Nations Control over N America 1750-2008 gif North America Image Political Evolution of Central America and the Caribbean 1700 and on gif Central America Image Balkans_Animation_1800-2008 gif Balkans Image Non-Native American Nations Control over South America 1700 and on gif South America </GALLERY> Non-Native American Nations Control over South America ” 1700 and on Own 2008-04 Esemono pages Guiana Arbitration Tribunal Paris 1899 Videos of maps Videos of history Jesuit Reductions Computer generated videos Slideshow videos Animated maps showing changing boundaries over time | ||||