MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
| View Original: | Partie_Occidentale_de_la_Nouvelle_France_ou_du_Canada.jpg (1250x1005) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | www.flickr.com | More Like This | ||
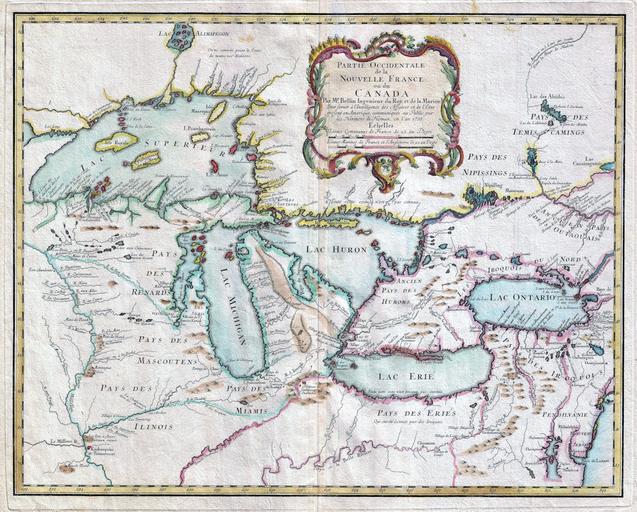
| Keywords: drawing sketch map text writing cartoon photo border painting 1755 Bellin Map of the Great Lakes - Geographicus - GreatLakes; Wikipedia Commons en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:1755_Bellin_Map_of_the_Great_L... (accessed 12/18/2016) by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin (1703–1772) Official Hydrographer (chief cartographer) of the French King. A rare and extremely influential 1755 map of the Great Lakes drawn by Jacques Nicholas Bellin. This map, which appeared in the 1755 issue of the Homann Heirs Atlas Major , covers all five of the Great Lakes as well as the adjacent Indian lands and the English colonies of Pennsylvania, New Jersey and New York. Cartographically this map offers a number of important innovations and is largely derived from Bellin’s very similar map of 1745. The plate was acquired and reissued by Homann Heirs in 1755 in response to European interest in the French and Indian War which started one year prior in 1754. Bellin based this map on the most advanced French cartographic intelligence available at the time. Heidenrich and Dahl consider this map to constitute “the first new material pertaining to New France to appear since the maps of Guillaume de L'Isle three decades earlier. Most notably this map incorporates the work of the French fur trader and explorer Sieur la Verendrye and the explorer-missionary Father Pierre de Charlevoix. From Verendrye , Bellin is able to extract a significantly advanced view, over De L’Isle, of the form of the Great Lakes and their client river systems. He also relies on Verendrye’s journals with regard to the placement of numerous Indian nations and villages. Charlevoix is generally regarded as Bellin’s source for his curious choice to include several fictional islands in Lake Superior, including I. Philippeaux, I. Pontchartrain, and I. St. Anne. This map is the first, though hardly the last, to depict these ghost islands which baffled explorers until the early 19th century. A quick overview of this map will reveal a territory that is very much dominated by various American Indian nations though nominally under a tenuous French hegemony. The vast lands of the Miami, the Iroquois, the Erie, the Huron, the Renard, the Mascouten, and the Illinois overwhelm tiny bastions of French power in the form of various forts and missions. Among these are Fort Frontenac, Fort Niagara, Mission Francois Xavier, and the fledgling “R. et Port de Checagou,” the future site of Chicago. The French, without the vast colonial resources of the English and Spanish, relied heavily on alliance with, rather than outright control of, indigenous populations. Thus it is understandable why the American Indian nations of this region were quick to throw their lot in with the French against the domineering English during the French and Indian War. In the lower right hand quadrants of this map Bellin employs a common cartographic trick to flatter his royal patrons in Paris. By diminishing the proportional size of the English colonial holdings in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Virginia and New York, Bellin, at least metaphorically, advances the supremacy of the French dominions in North America. In addition to its advanced mapping of the Great Lakes, its introduction of the ghost islands of Lake Superior, and its incorporation of the most recent explorations in the region, this map enjoys lasting significance due to John Mitchell’s use of it in compiling his important wall map, A Map of the British & French Dominions in North America . Mitchell’s monumental cartographic masterpiece was used in 1783 to define the boundaries between Canada and the post-Revolutionary United States, forming the basis for national borders that are still in effect today. Height: 17.5 in (44.5 cm). Width: 21.5 in (54.6 cm). acques-Nicolas Bellin (1703 - 1772) was one of the most important cartographers of the 18th century. With a career spanning some 50 years, Bellin is best understood as geographe de cabinet and transitional mapmaker spanning the gap between 18th and early 19th century cartographic styles. His long career as Hydrographer and Ingénieur Hydrographe at the French Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine resulted in hundreds of high quality nautical charts of practically everywhere in the world. A true child of the Enlightenment Era, Bellin's work focuses on function and accuracy tending in the process to be less decorative than the earlier 17th and 18th century cartographic work. Unlike many of his contemporaries, Bellin was always careful to cite his references and his scholarly corpus consists of over 1400 articles on geography prepared for Diderot's Encyclopedie. Bellin, despite his extraordinary success, may not have enjoyed his work, which is described as "long, unpleasant, and hard." In addition to numerous maps and charts published during his lifetime, many of Bellin's maps were updated (or not) and published posthumously. He was succeeded as Ingénieur Hydrographe by his student, also a prolific and influential cartographer, Rigobert Bonne. Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest before converting to Protestantism in 1687. Following his conversion, Homann moved to Nuremberg and found employment as a notary. Around 1693 Homan briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Afterwards he returned to Nuremberg where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. The Homann firm, due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, was able to undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching the diversity and quality of their output. By 1715 Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles the VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with a number of important advantages including access to the most up to date cartographic information as well as the "Privilege". The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to a few individuals by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though not as sophisticated as modern copyright legislation, the Privilege did offer a kind of limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription "Cum Priviligio" or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1726, the management of the firm passed to his son Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger and Johann Michael Franz, and that it would publish only under the name Homann Heirs. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc..) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo in 1848. - See more at: www.geographicus.com/P/AntiqueMap/GreatLakes-bellin-1755#... 1755 Bellin Map of the Great Lakes - Geographicus - GreatLakes; Wikipedia Commons en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:1755_Bellin_Map_of_the_Great_L... (accessed 12/18/2016) by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin (1703–1772) Official Hydrographer (chief cartographer) of the French King. A rare and extremely influential 1755 map of the Great Lakes drawn by Jacques Nicholas Bellin. This map, which appeared in the 1755 issue of the Homann Heirs Atlas Major , covers all five of the Great Lakes as well as the adjacent Indian lands and the English colonies of Pennsylvania, New Jersey and New York. Cartographically this map offers a number of important innovations and is largely derived from Bellin’s very similar map of 1745. The plate was acquired and reissued by Homann Heirs in 1755 in response to European interest in the French and Indian War which started one year prior in 1754. Bellin based this map on the most advanced French cartographic intelligence available at the time. Heidenrich and Dahl consider this map to constitute “the first new material pertaining to New France to appear since the maps of Guillaume de L'Isle three decades earlier. Most notably this map incorporates the work of the French fur trader and explorer Sieur la Verendrye and the explorer-missionary Father Pierre de Charlevoix. From Verendrye , Bellin is able to extract a significantly advanced view, over De L’Isle, of the form of the Great Lakes and their client river systems. He also relies on Verendrye’s journals with regard to the placement of numerous Indian nations and villages. Charlevoix is generally regarded as Bellin’s source for his curious choice to include several fictional islands in Lake Superior, including I. Philippeaux, I. Pontchartrain, and I. St. Anne. This map is the first, though hardly the last, to depict these ghost islands which baffled explorers until the early 19th century. A quick overview of this map will reveal a territory that is very much dominated by various American Indian nations though nominally under a tenuous French hegemony. The vast lands of the Miami, the Iroquois, the Erie, the Huron, the Renard, the Mascouten, and the Illinois overwhelm tiny bastions of French power in the form of various forts and missions. Among these are Fort Frontenac, Fort Niagara, Mission Francois Xavier, and the fledgling “R. et Port de Checagou,” the future site of Chicago. The French, without the vast colonial resources of the English and Spanish, relied heavily on alliance with, rather than outright control of, indigenous populations. Thus it is understandable why the American Indian nations of this region were quick to throw their lot in with the French against the domineering English during the French and Indian War. In the lower right hand quadrants of this map Bellin employs a common cartographic trick to flatter his royal patrons in Paris. By diminishing the proportional size of the English colonial holdings in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Virginia and New York, Bellin, at least metaphorically, advances the supremacy of the French dominions in North America. In addition to its advanced mapping of the Great Lakes, its introduction of the ghost islands of Lake Superior, and its incorporation of the most recent explorations in the region, this map enjoys lasting significance due to John Mitchell’s use of it in compiling his important wall map, A Map of the British & French Dominions in North America . Mitchell’s monumental cartographic masterpiece was used in 1783 to define the boundaries between Canada and the post-Revolutionary United States, forming the basis for national borders that are still in effect today. Height: 17.5 in (44.5 cm). Width: 21.5 in (54.6 cm). acques-Nicolas Bellin (1703 - 1772) was one of the most important cartographers of the 18th century. With a career spanning some 50 years, Bellin is best understood as geographe de cabinet and transitional mapmaker spanning the gap between 18th and early 19th century cartographic styles. His long career as Hydrographer and Ingénieur Hydrographe at the French Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine resulted in hundreds of high quality nautical charts of practically everywhere in the world. A true child of the Enlightenment Era, Bellin's work focuses on function and accuracy tending in the process to be less decorative than the earlier 17th and 18th century cartographic work. Unlike many of his contemporaries, Bellin was always careful to cite his references and his scholarly corpus consists of over 1400 articles on geography prepared for Diderot's Encyclopedie. Bellin, despite his extraordinary success, may not have enjoyed his work, which is described as "long, unpleasant, and hard." In addition to numerous maps and charts published during his lifetime, many of Bellin's maps were updated (or not) and published posthumously. He was succeeded as Ingénieur Hydrographe by his student, also a prolific and influential cartographer, Rigobert Bonne. Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest before converting to Protestantism in 1687. Following his conversion, Homann moved to Nuremberg and found employment as a notary. Around 1693 Homan briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Afterwards he returned to Nuremberg where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. The Homann firm, due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, was able to undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching the diversity and quality of their output. By 1715 Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles the VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with a number of important advantages including access to the most up to date cartographic information as well as the "Privilege". The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to a few individuals by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though not as sophisticated as modern copyright legislation, the Privilege did offer a kind of limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription "Cum Priviligio" or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1726, the management of the firm passed to his son Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger and Johann Michael Franz, and that it would publish only under the name Homann Heirs. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc..) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo in 1848. - See more at: www.geographicus.com/P/AntiqueMap/GreatLakes-bellin-1755#... | ||||